.png)
The 2020 Equinoxes
|
|
There are only two times of the year when the Earth's axis is tilted neither toward nor away from the sun, resulting in a "nearly" equal amount of daylight and darkness at all latitudes. These events are referred to as Equinoxes and will occur on March 19th at 9:49 pm MDT (Vernal Equinox - the first day of Spring) and again on September 22nd at 7:30 am MDT (Autumnal Equinox - the first day of fall). The word equinox is derived from two Latin words - aequus (equal) and nox (night). At the equator, the sun is directly overhead at noon on these two equinoxes. The "nearly" equal hours of day and night is due to refraction of sunlight. or a bending of the light's rays that causes the sun to appear above the horizon when the actual position of the sun is below the horizon. Additionally, the days become a little longer at the higher latitudes (those at a distance from the equator) because it takes the sun longer to rise and set. Therefore, on the equinox and for several days before and after the equinox, the length of day will range from about 12 hours and six and one-half minutes at the equator, to 12 hours and 8 minutes at 30 degrees latitude, to 12 hours and 16 minutes at 60 degrees latitude. |
|
|
|
|
The 2020 Solstices
|
|
The Seasons
|
|
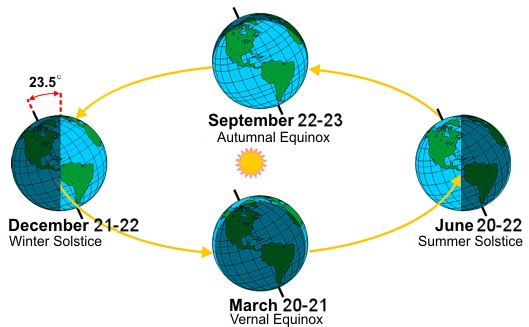
We all know that the Earth makes a complete revolution around the sun once every 365 days, following an orbit that is elliptical in shape. This means that the distance between the Earth and Sun, which is 93 million miles on average, varies throughout the year. During the first week in January, the Earth is about 1.6 million miles closer to the sun. This is referred to as the perihelion. The aphelion, or the point at which the Earth is about 1.6 million miles farther away from the sun, occurs during the first week in July. This fact may sound counter to what we know about seasons in the Northern Hemisphere, but actually the difference is not significant in terms of climate and is NOT the reason why we have seasons. Seasons are caused by the fact that the Earth is tilted on its axis by 23.5°. The tilt's orientation with respect to space does not change during the year; thus, the Northern Hemisphere is tilted toward the sun in June and away from the sun in December, as illustrated in the graphic below. |
 |