
A rapidly-intensifying winter storm continues to bring heavy snow, high winds, and blizzard conditions over the Upper Midwest and Great Lakes through today. An Arctic front will lead in a period of gusty to high winds and sharply colder temperatures over the entire eastern U.S. Heavy lake effect snow is then expected from Lakes Erie and Ontario through New Year's Day. Read More >
Overview
|
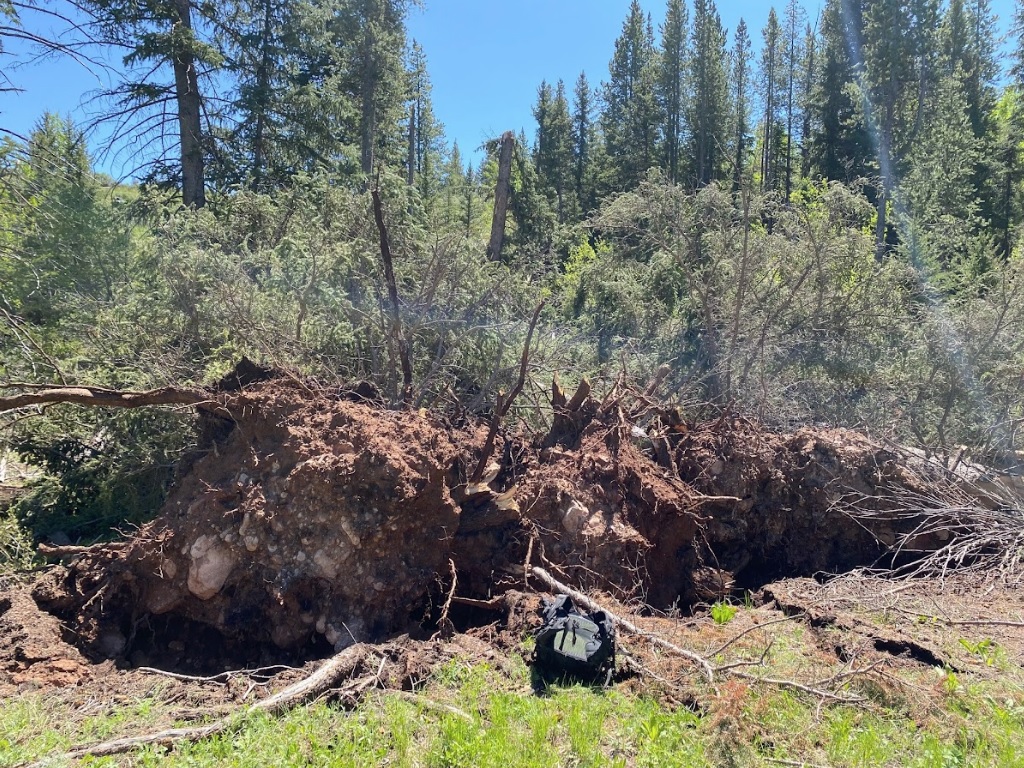
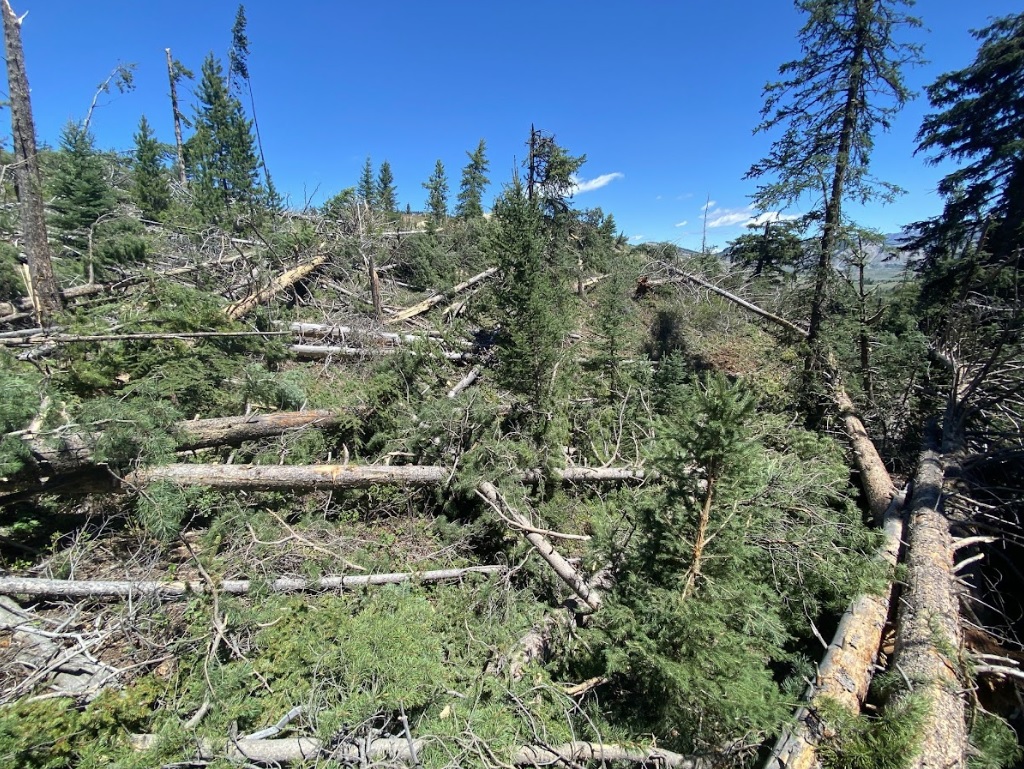
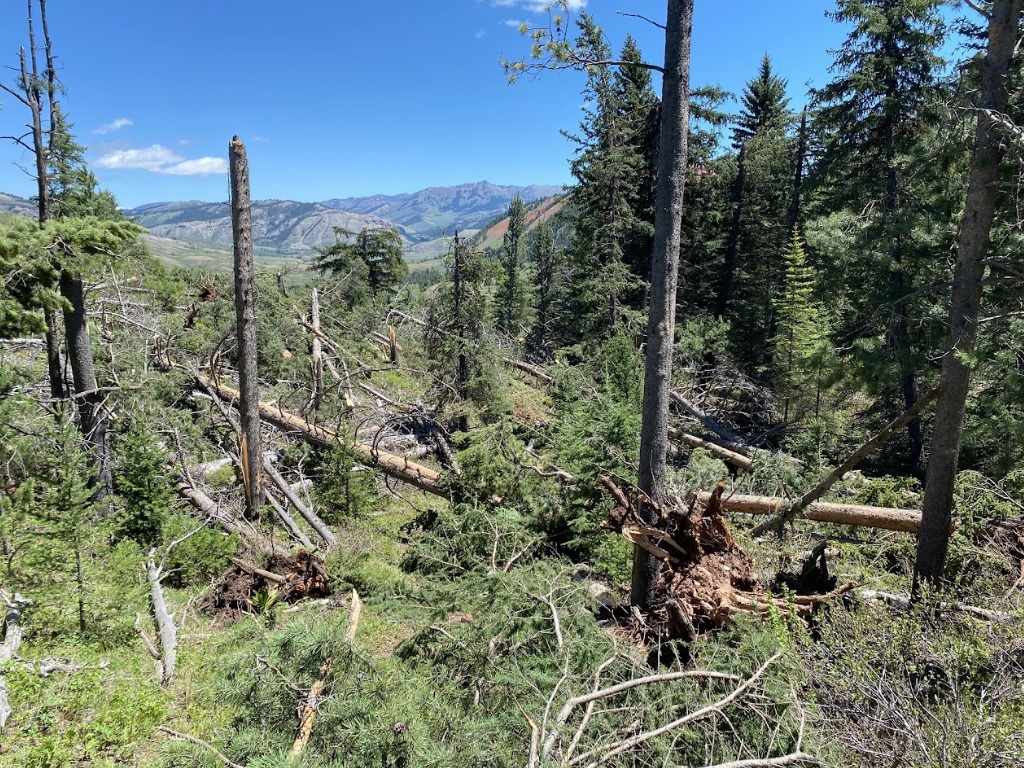
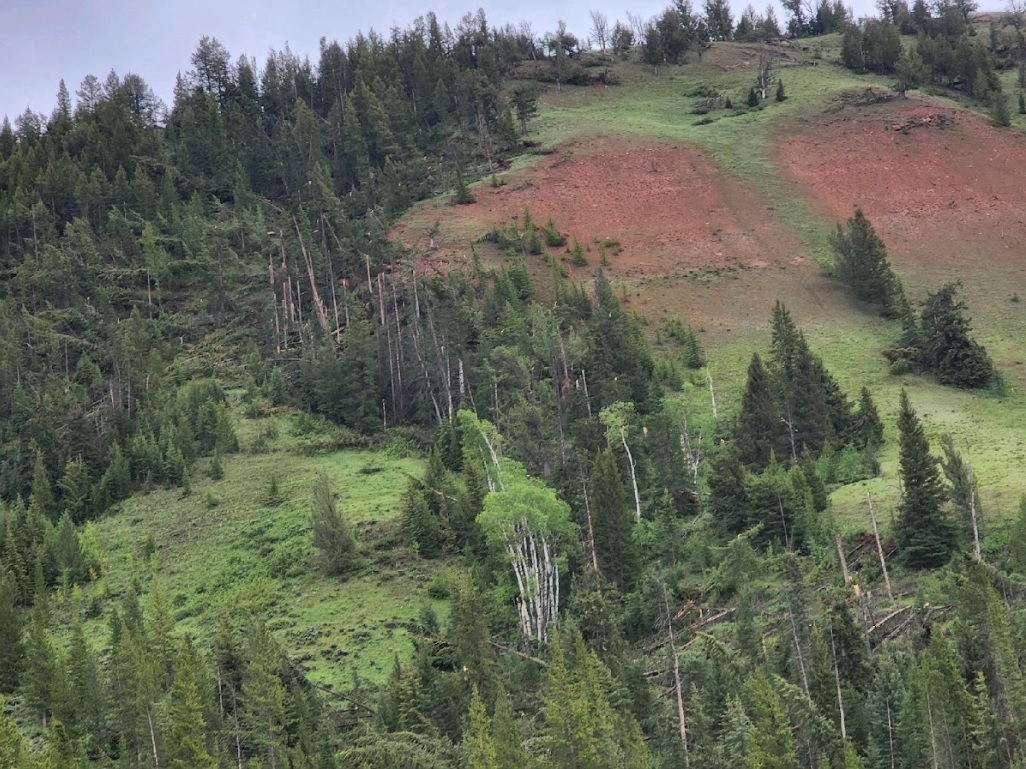
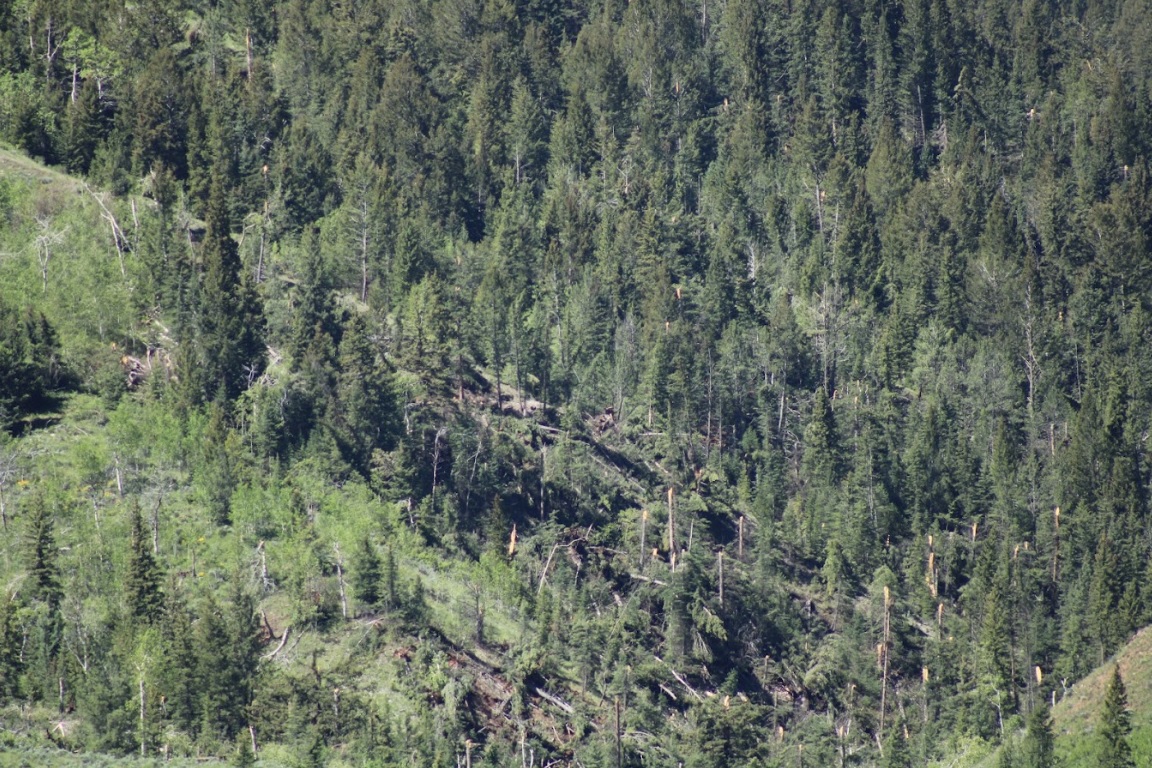
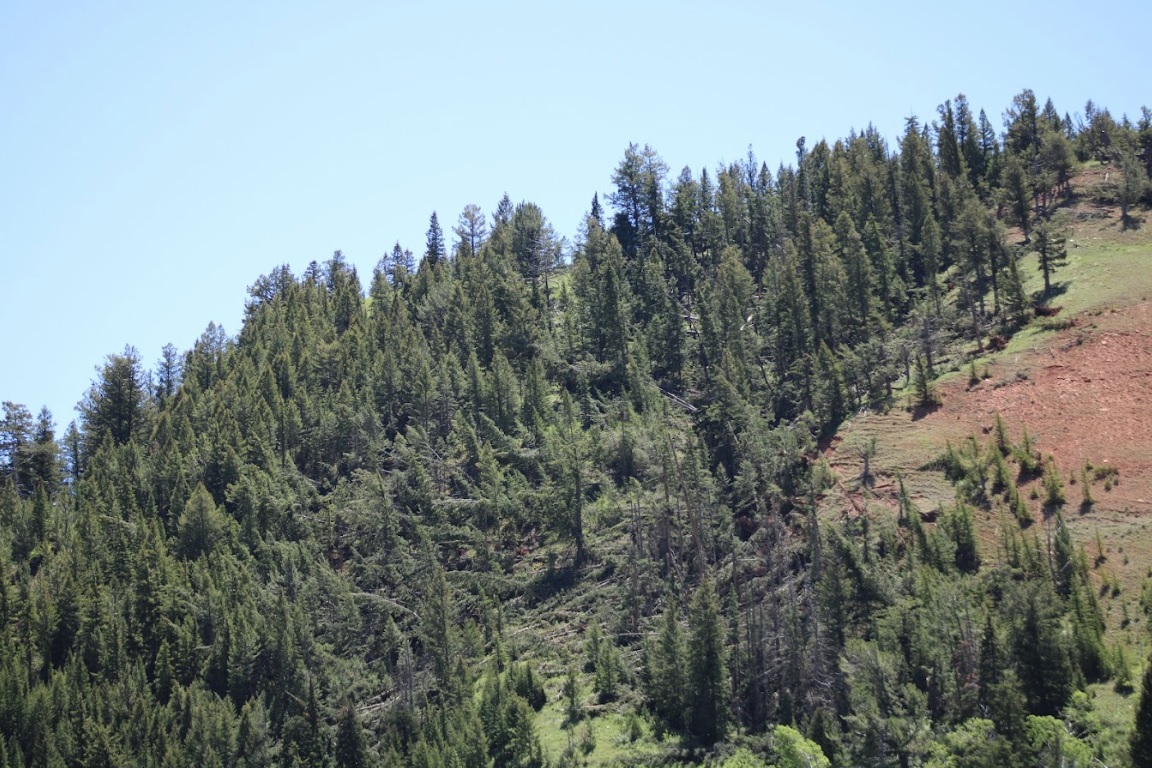
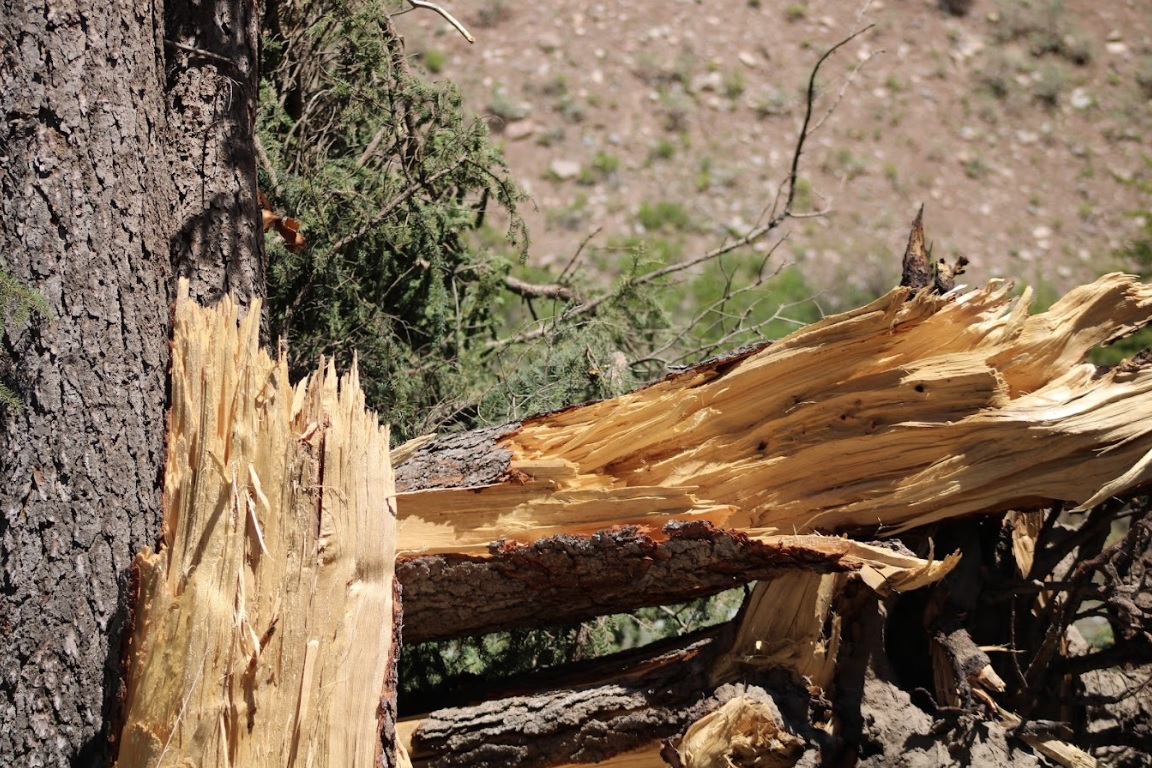
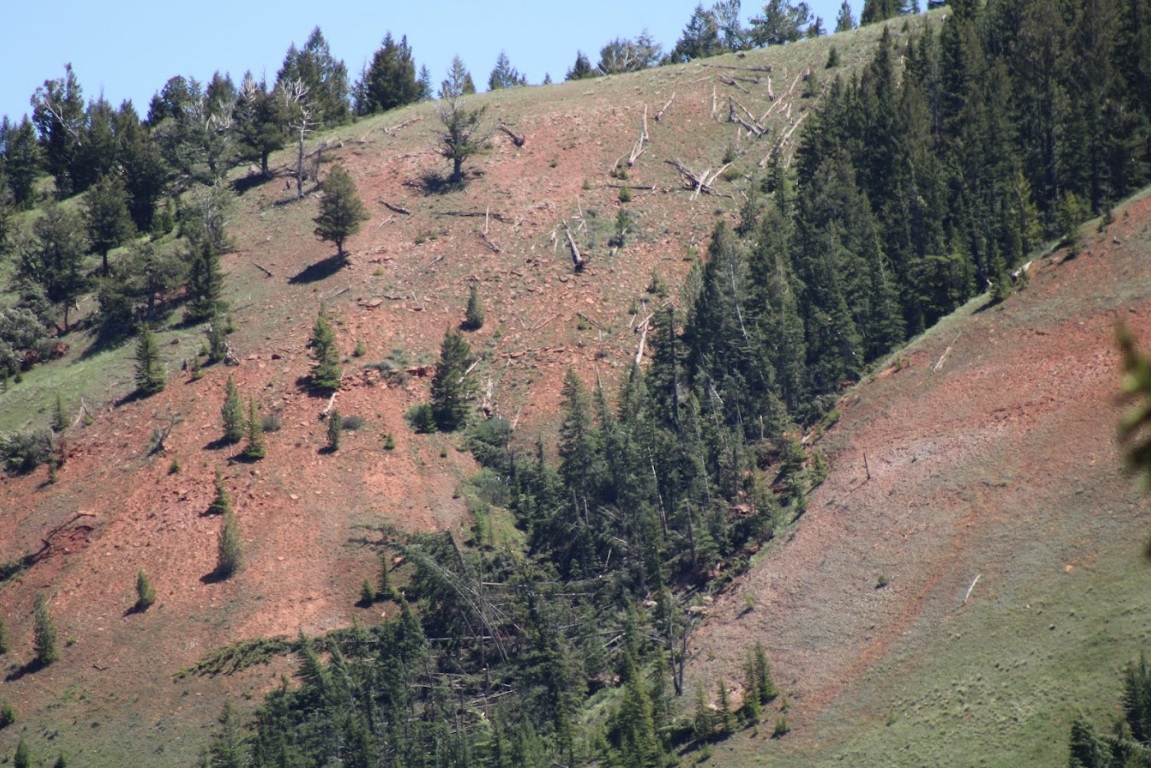
On June 12th, 2022, a supercell thunderstorm moved from southwest to northeast over the Gros Ventre Range in the Bridger-Teton National Forest. Several months after this event, Bridger Teton National Forest staff reached out to the NWS Riverton office and shared images and helicopter footage of a distinct path of tree damage through a thickly-forested high-elevation area that coincided with the supercell path from June 12th. This area of widespread tree damage is relatively inaccessible and was not viewable to the NWS damage survey team that visited the Gros Ventre River valley immediately following the event. Post-event interrogation of radar imagery from the event showed a strong rotation couplet above this damage area. After consulting with experienced NWS staff with decades of tornado-damage-determining experience, this tree damage was determined to have been caused by a tornado. The tree fall pattern and path were consistent with strong tornadic rotation. The EF2 designation comes from looking at the softwood damage indicator of the Enhanced Fujita Scale. Pictures show thousands of pine trees snapped at various heights, with hardly any trees remaining upright. There was some evidence of debarking in photos as well. For this reason, wind speeds were estimated to be between 128 and 131 mph, based on the upper bound for softwood trunks snapped and the expected damage for softwood debarked. Path length and width were determined from polar-orbiting satellite data from the summer months after the event. Notable decreases in vegetation could be seen, with a clearly defined damage path in satellite imagery as well. This tornado is notable for being the second known tornado to occur in Teton County, as well as being a tornado that occurred in complex terrain at relatively high elevations between roughly 8000 and 9000 feet. (Note that the photos tab below includes pictures from the nearby Gros Ventre River valley, where related severe thunderstorm wind gust damage was observed.)
|
(USDA Forest Service - Teton Interagency Helitack) |
Tornadoes:
|
Tornado -
Track Map 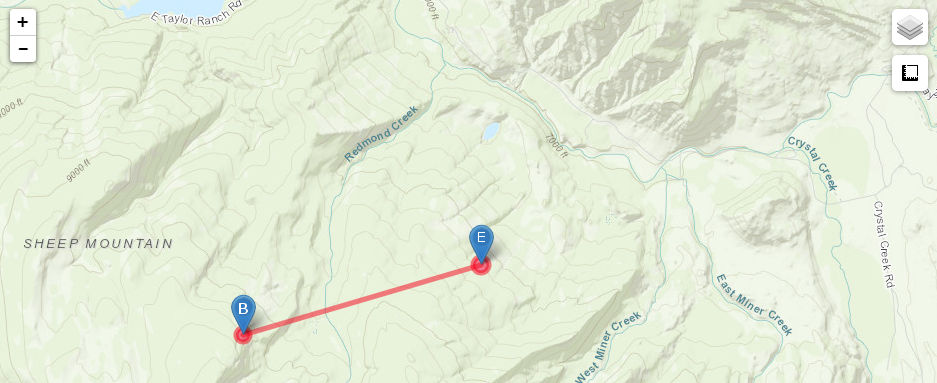
Damage Track. "B" denotes the beginning of the tornado track, and "E" dontes the end. |
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
The Enhanced Fujita (EF) Scale classifies tornadoes into the following categories:
| EF0 Weak 65-85 mph |
EF1 Moderate 86-110 mph |
EF2 Significant 111-135 mph |
EF3 Severe 136-165 mph |
EF4 Extreme 166-200 mph |
EF5 Catastrophic 200+ mph |
 |
|||||
Photos
 |
 |
 |
 |
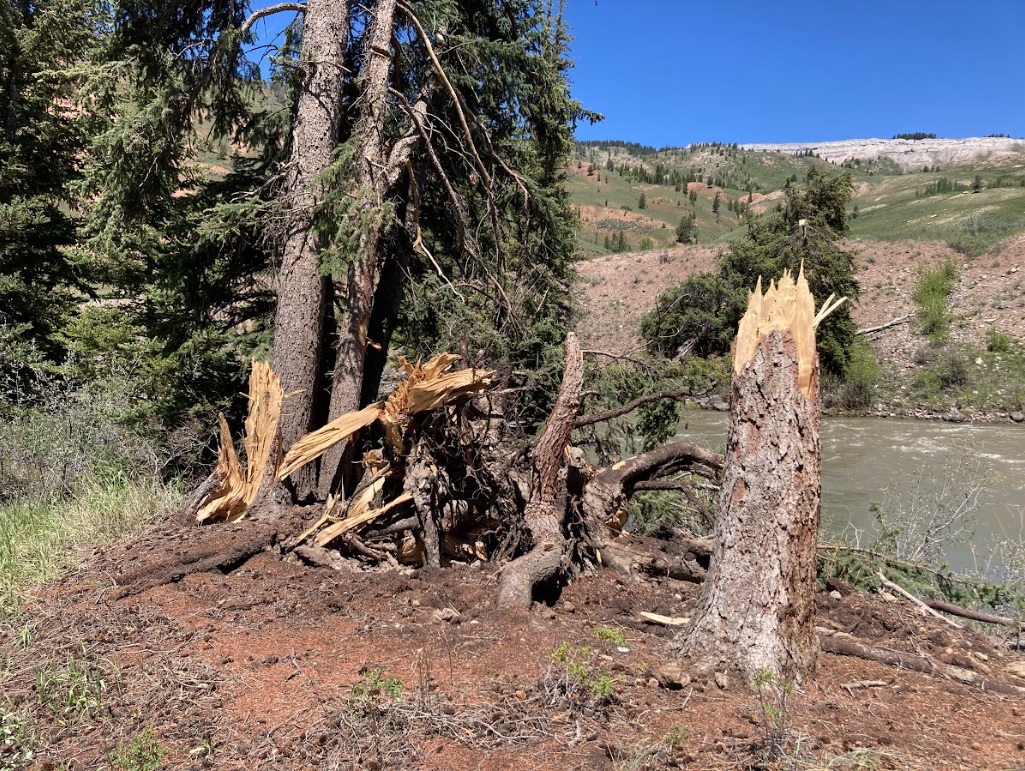
| Uprooted tree with backpack for size reference (Tim Farris) |
Damaged trees in the Bridger-Teton National Forest (Tim Farris) |
Damaged trees in the Bridger-Teton National Forest (Tim Farris) |
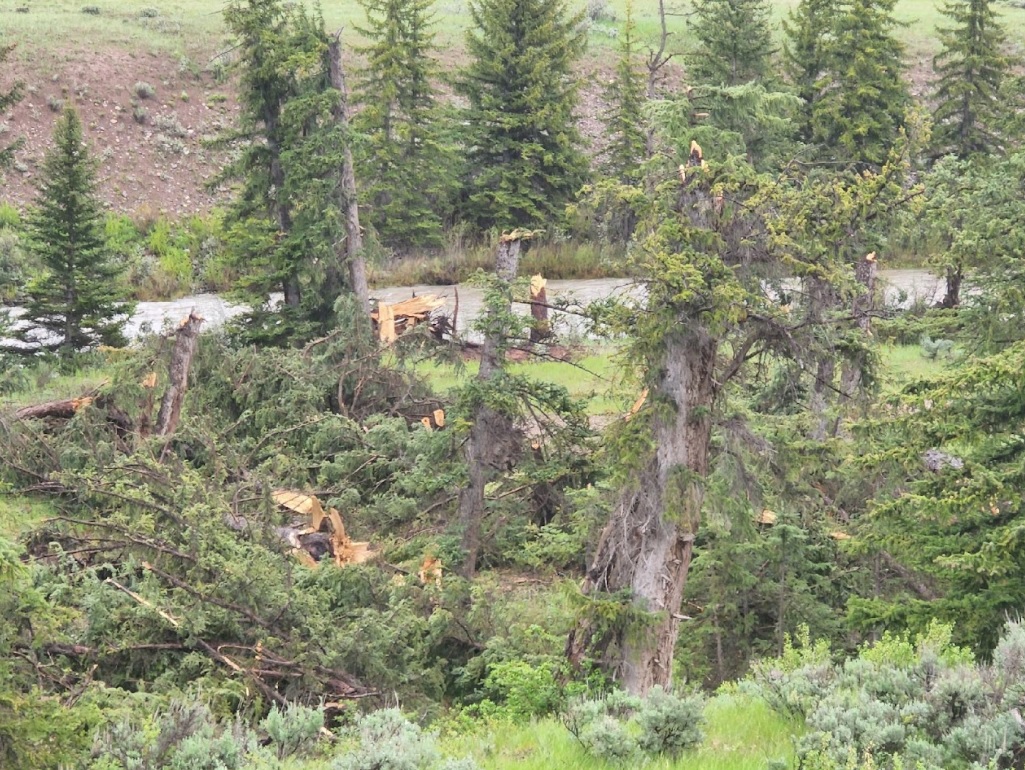
Tree damage on north aspect as seen looking south from the Gros Ventre River valley (Dave Lipson) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
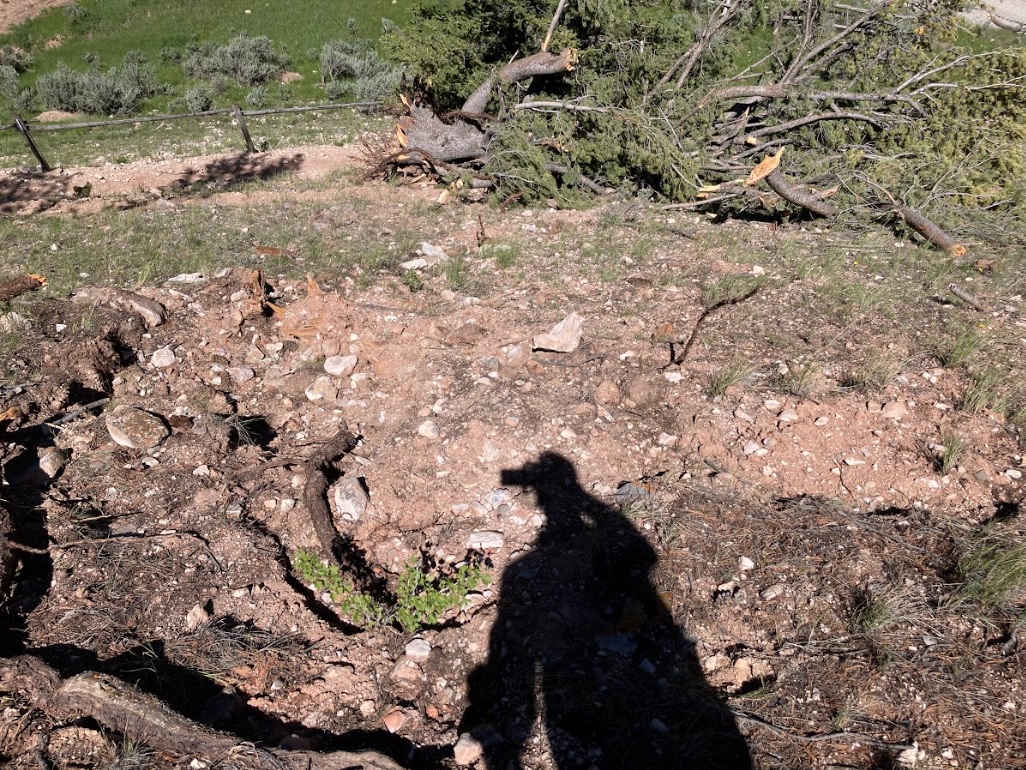
| Tree damage near the Crystal Creek campground (NWS Survey) |
Tree damage along the Gros Ventre River (NWS Survey) |
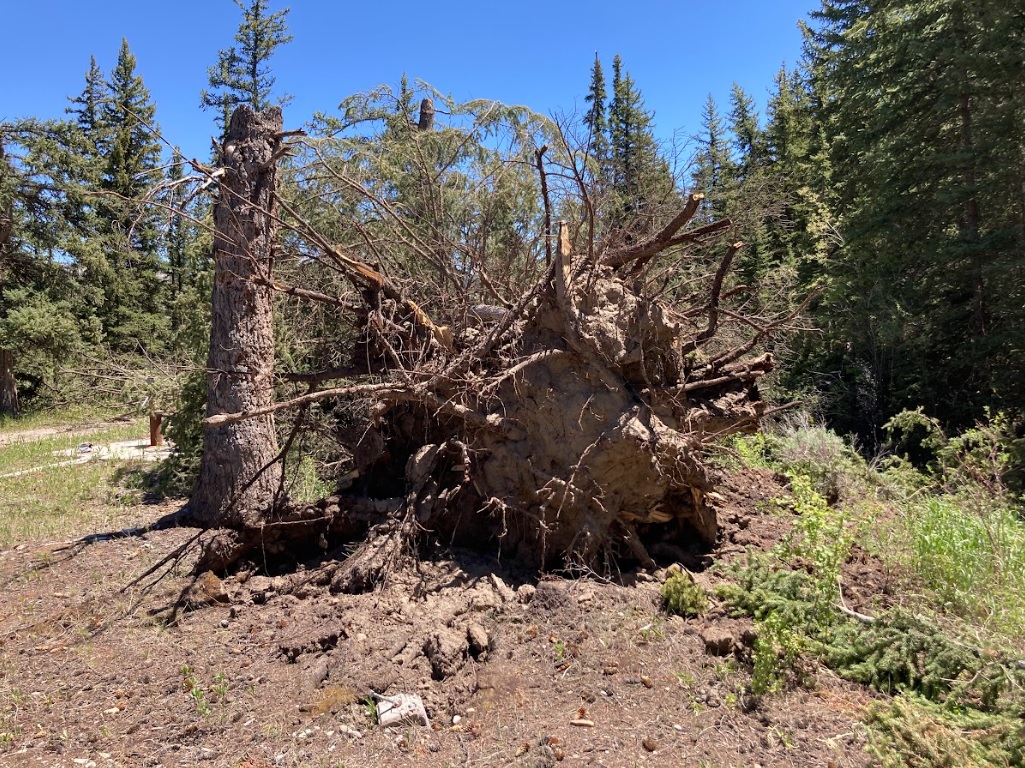
Uprooted tree near the Crystal Creek campground (NWS Survey) |
Tree damage along the Gros Ventre River (Dave Lipson) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Tree damage on north aspect as seen looking south from the Gros Ventre River valley (NWS Survey) |
Tree damage on north aspect as seen looking south from the Gros Ventre River valley (NWS Survey) |
Tree damage near the Crystal Creek campground (NWS Survey) |
Tree damage on north aspect as seen looking south from the Gros Ventre River valley (NWS Survey) |
 |
Media use of NWS Web News Stories is encouraged! Please acknowledge the NWS as the source of any news information accessed from this site. |
 |