SEVERE THUNDERSTORMS
What classifies a "severe" thunderstorm?
 A thunderstorm is classified as "severe" by the National Weather Service when it produces damaging wind gusts in excess of 58 mph or hail one inch in diameter or larger. An occurrence of a tornado will also classify a thunderstorm as severe. More information about A thunderstorm is classified as "severe" by the National Weather Service when it produces damaging wind gusts in excess of 58 mph or hail one inch in diameter or larger. An occurrence of a tornado will also classify a thunderstorm as severe. More information about
tornadoes is given in the Tornado section.
How do severe thunderstorms impact southeast Texas?
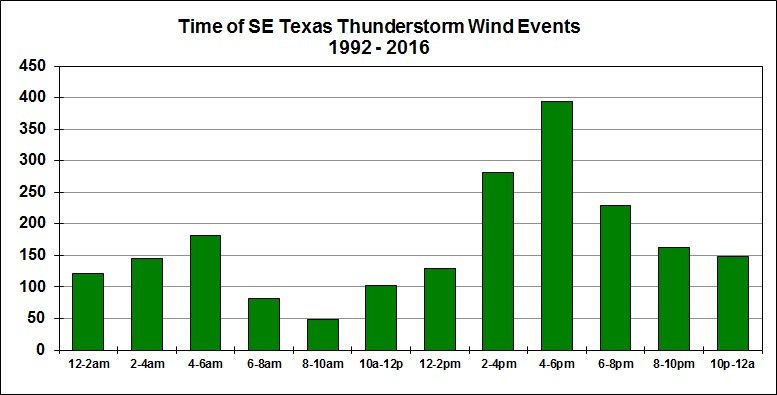
While severe thunderstorms are most common in the spring, they can occur just about any time of year in southeast Texas. On average, southeast Texas experiences 50 to 60 days a year with thunderstorms. Severe thunderstorms occur on about a third of those days. Severe storms can occur just about any time of day in southeast Texas, but are most common in the afternoon and evening hours.
Severe weather threats:
- Downbursts
A downburst is a rapidly descending current of air beneath a thunderstorm. Downburst winds are often referred to as "straight-line" winds. Severe downbursts produce wind gusts from 60 mph to more than 100 mph. The damage can be comparable to a tornado but the pattern of damage is typically different. Downburst damage is far more common in southeast Texas than tornado damage.
- Large Hail
Hail is formed as strong rising currents of air within a storm (updrafts) carry water droplets to a height where freezing occurs. The ice particles travel upward and downward through the storm several times, growing in size. Once they become too heavy to be supported by the storm's updraft, they fall to the ground as hail. Hail of 3/4 inch in diameter or larger classifies "large" or damaging hail. Hail sizes are usually referred to everyday objects to make it easier to estimate hail size.
| Examples of hail sizes: |
| pea sized |
0.25 inch |
| penny sized |
0.75 inch |
| nickel sized |
0.88 inch |
| quarter sized |
1.00 inch
(classifies storm as severe) |
| golfball sized |
1.75 inches |
| baseball sized |
2.75 inches |
|
|
Hail greater than baseball size is rare in southeast Texas but softball sized hail has been observed on occasion. Hail can damage crops and can also cause damage to automobiles and rooftops.
- Tornadoes
Tornadoes are another threat from severe thunderstorms. See the Tornado section for more information.
- Cloud-to-Ground Lightning
Severe thunderstorms can produce extremely dangerous lightning. See the Lightning section for more information.
- Flash Flooding
Heavy rains from severe thunderstorms can produce flash flooding. See the Floods/Flash Floods section for more information.
What were some severe weather events that impacted Southeast Texas?
- April 2, 2013
- A severe thunderstorm produced baseball to softball sized hail (up to 4.50 inches) in Hitchcock (Galveston County). The central and western parts of the town received extreme damage to vehicles and home roofs and windows. There was also significant damage to the Midway Church, a fire station, and in two trailer parks. Seven Hitchcock police cars were severely damaged by the large hail.
- October 22, 2008
- Showers and thunderstorms developed along and ahead of a strong cold front and produced golf ball size hail (up to 1.75 inches) in Houston (Harris County) near the intersection of Beltway 8 North and the Hardy Toll Road.
- May 4, 2006
- A severe thunderstorm developed in the afternoon and produced large hail (up to 3.00 inches - the size of tea cups) in the Champions Forest Subdivision near Houston Hooks Airport.
- May 8, 2005
- Severe thunderstorms with strong damaging winds and large hail moved across the southern half of southeast Texas with damage observed from the El Campo and Wharton area (trees and power lines down, roof damage and a hanger with an airplane inside destroyed) eastward to the coast. Further to the east (Brazoria County), strong winds downed trees and blew roofs off mobile homes in Rosharon, Danbury and Liverpool. In Alvin, a metal shed and billboards were also downed by the wind. Near the coast in Galveston County, large hail (up to golf ball size) fell in Texas City, and strong winds downed large trees and damaged property from League City to Dickinson to Galveston Island. On the Island, there was building damage along the Port of Galveston, vehicles were blown off the road and trees were downed. One home was shifted about ten feet into another home next door dislodging it from its piers (both homes were Galveston 1900 Storm survivors).
- December 23, 2002
- The combination of abundant low level moisture, a strong upper level storm system and a warm front helped to produce nearly fifty severe weather events across Southeast Texas including tornadoes in Colorado, Burleson, Washington, Brazos, Grimes, Madison, Montgomery and San Jacinto counties. Large hail (up to 1.75 inches) was observed mainly north and west of the Houston area. Locations from Houston to the beaches felt the brunt of this event in the evening when a squall line moved rapidly eastward across Harris county and toward the coast and produced 60 to 80 mph winds.
- November 23-24, 2000
- Three tornadoes struck the Houston area on Thanksgiving night. An F1 tornado struck Katy injuring one person, flipping over two office trailers and damaging several homes. Pasadena was also struck by an F1 tornado which damaged a church and two schools, several homes in a neighborhood, and tore the walls off of a strip shopping center. Another F0 tornado struck Conroe, downing trees and tearing the steeple off a church.
- May 1-2, 2000
- A storm system produced widespread severe thunderstorms over the southern half of Southeast Texas during the overnight hours of the 1st and the early morning hours of the 2nd. Widespread wind damage impacted Harris, Fort Bend, Wharton, Brazoria and Galveston counties. The worst damage occured at Clover Field in Pearland where several planes were overturned and two small airplane hangers were destroyed. At Scholes Field in Galveston, several small planes were also overturned and the NOAA P-3 research aircraft was damaged. A massive hailstorm with baseball-sized hail struck Conroe producing over $10 million in damage.
National Weather Service Severe Thunderstorm Products:
- HAZARDOUS WEATHER OUTLOOK
Issued by the local National Weather Service office daily at 7 AM. Usually covers a large portion of southeast Texas. Outlines the reasons for the potential for severe weather, the area that could be affected and the time that severe weather is anticipated.
- SEVERE THUNDERSTORM WATCH
Issued by the Storm Prediction Center in Norman, OK. Usually covers a large area (such as all or a portion of southeast Texas) and lasts for 6 to 8 hours. A SEVERE THUNDERSTORM WATCH means that conditions are favorable for severe thunderstorms that may produce large hail, damaging wind, dangerous lightning, or possibly tornadoes.
- SEVERE THUNDERSTORM WARNING
Issued by the local National Weather Service office. Usually covers a small area (one or a few counties) and has a short duration of 30 minutes to an hour. A SEVERE THUNDERSTORM WARNING means that a severe thunderstorm has been detected by radar, or reports of severe weather have been received by the National Weather Service in the area covered by the warning. The warnings are broadcast over NOAA Weather Radio and are usually scrolled on local television stations. The warnings are also relayed to local emergency management and public safety officials who can activate emergency procedures to help protect the public. If a warning is issued for your area, take action immediately!!
- SEVERE WEATHER STATEMENT
Follow-up information on a WARNING.
What can you do to be prepared for severe weather?
- Know the county that you live in and the names of nearby major cities. SEVERE THUNDERSTORM WARNINGS are issued on a county by county basis with the names of major cities highlighted in the warnings.
- Have a NOAA Weather Radio in your home or place of business. Some receivers are specially built to alarm any time a severe weather Watch or Warning is issued by the National Weather Service.
- Make sure you are aware of the best spot in your home to take shelter from severe weather. The most appropriate place is usually an interior room on the lowest floor of your home and away from windows. If you know severe weather is approaching or a SEVERE THUNDERSTORM WARNING is issued, seek shelter immediately!! Being in a sturdy building on the lowest floor and away from windows is the only safe place in a severe thunderstorm!! Automobiles, boats, or out in the open are not safe places in severe thunderstorms.
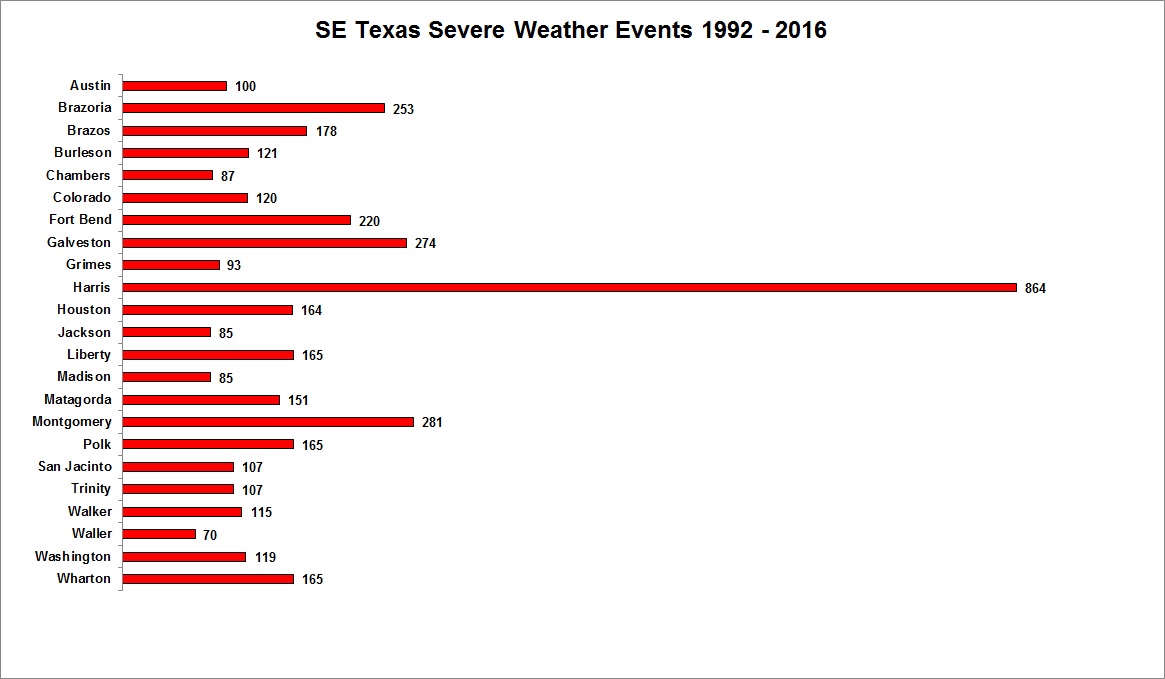
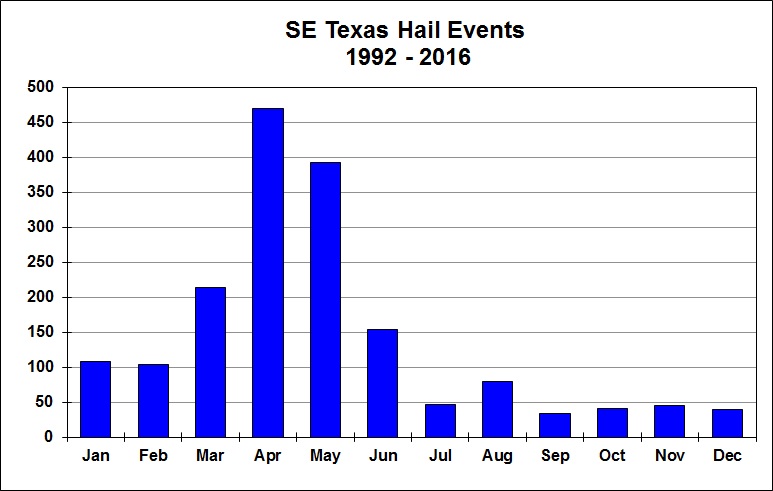
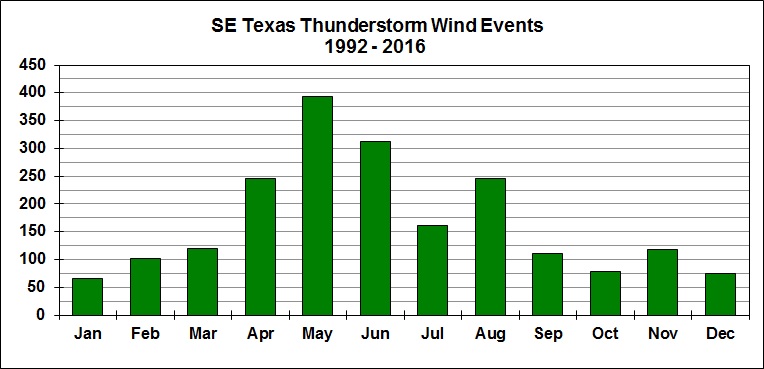
Severe Thunderstorms Statistics for Southeast Texas (1992-2016)
|
 A thunderstorm is classified as "severe" by the National Weather Service when it produces damaging wind gusts in excess of 58 mph or hail one inch in diameter or larger. An occurrence of a tornado will also classify a thunderstorm as severe. More information about
A thunderstorm is classified as "severe" by the National Weather Service when it produces damaging wind gusts in excess of 58 mph or hail one inch in diameter or larger. An occurrence of a tornado will also classify a thunderstorm as severe. More information about



